
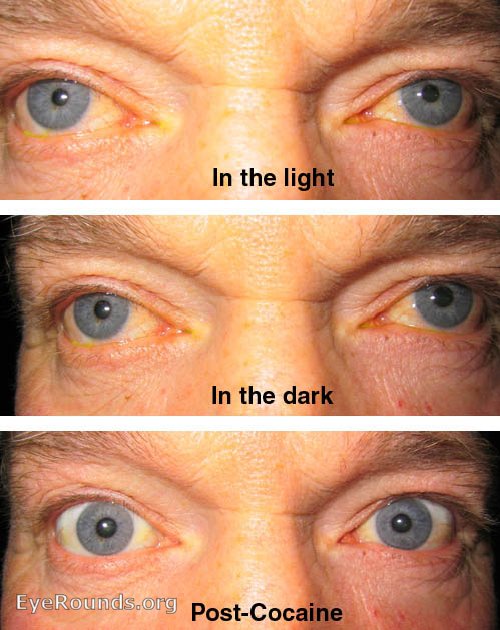
Immediately on dimming of the light in Horner syndrome, one pupil will dilate more slowly than the other and the magnitude of the anisocoria will be observed to increase (dilation lag). With the light on, both pupils will be miotic and some anisocoria may be observed. The anisocoria of Horner syndrome is best examined with the patient fixating on a distance object and observing both pupils as a bright light is alternately turned on and off. The light and near pupillary reactions are intact. The anisocoria of Horner syndrome is more apparent in dim illumination, and the affected pupil shows a lag in dilation on dimming of the lights. The classic triad of findings includes ptosis, miosis, and anhidrosis on the affected side. Pharmacologic miosis occurs with echothiophate iodide or pilocarpine.Ī lesion at any point along the sympathetic pathway for pupillary constriction results in Horner syndrome. Pharmacologic testing with 1% pilocarpine is useful for differentiating pharmacologic mydriasis from third cranial nerve palsy pupillary constriction occurs in third nerve palsy and does not occur with pharmacologic mydriasis. Pharmacologic mydriasis may occur with minimal exposure to atropine, cyclopentolate, or other parasympatholytic agents (e.g., accidental exposure to some pesticides). In cases of brainstem herniation and basilar meningitis, however, pupillary dilation may be the only sign of third nerve palsy.

Pupillary involvement in third nerve palsy is usually accompanied by ptosis and disturbances in ocular motility. Lesions of the parasympathetic or sympathetic system, if unilateral or asymmetrical, cause pupillary constriction or dilation and produce pupils that are unequal in size, termed anisocoria. Zitelli MD, in Zitelli and Davis' Atlas of Pediatric Physical Diagnosis, 2018 Anisocoria


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
